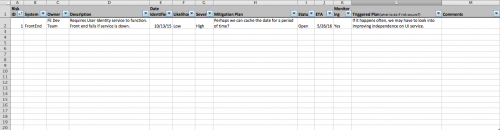
QA Symphony looks at 3 serious (but common) misconceptions about software testing:
- Testing is a Cost Center
- Legacy Tools are Good Enough
- Testing Is Easy
These are indeed very common.
Let me just briefly focus on the last one. Consider how quickly the complexity escalates. You are a building a simple website – nothing fancy, just some modern design and a few pages of content to represent your company. Let’s say you have just four pages: front page, about us, services, and contact us. You can quickly check how these four pages look in your browser. Easy right?
But wait. People use different browsers to access the web. So just checking it in your favorite one is not that enough. Which browsers should you test for? Let’s say we take the major ones – Google Chrome, Firefox, Microsoft Internet Explorer, and Safari. These should about cover us. Until now, your entire test was 4 page loads. Now you are multiplying it by 4 browsers. That’s 16 page loads. So far so good?
Not really. Each browser has multiple versions, which render pages differently. Not everyone is using the latest version. And new versions are released continuously. Let’s say you decided to support the latest two major versions of each browser. So now, that’s each browser times two. So 4 pages by 8 browser comes up to 32 page loads.
But we were just talking about the desktop browsers. You do want your site looking good on tablets and mobiles, right? Of course you do. What does that mean in terms of testing? Let’s say we support only iOS and Android – two major platforms, both for mobile and tablets. And we only support the default browser on each of those. That adds 4 more browsers.
By the way, when people browse on mobiles and tablets, sometimes they view your page holding a device vertically, and sometimes horizontally. You should probably test for those things as well. You know, just to make sure, nothing breaks through to the right, or requires too much scrolling down.
Remember that we are still talking about the simplest of all the websites here. Nothing fancy.
Let’s throw in an additional language. Here in Cyprus, for example, most websites are in English and Greek. Some add Russian. Some have a few languages. I’ve worked in the companies supporting over a dozen languages on the website. Each language means that you need to do more tests. In each of those browsers and on each of the supported devices.
You get my drift.
Something else. So far our tests were simple page loads, just to have a quick look whether or not the page looks fine. What if we have multiple tests per page. You want the page to look fine. But you also don’t want to have any syntax or grammar errors in the content. Especially in those foreign languages, that you don’t speak yourself. And you want the page to be optimized for search engines. And you want it to be fast (performance testing).
By now, you’ll probably give and agree that testing is not easy. Not even for the simplest of sites. Consider just how much more complicated it can get if your site is slightly more complex than that.
Remember that contact us page. That thing was just showing the company mailing address and the phone number. Now you want an integrated Google Map and a contact us form. Nothing wrong with that, right?
Well. Google services are banned in many countries. Will your contact us page still work if the user cannot access the Google Maps service? You’ll need to test for that. What about your contact form? Does it actually work? You can’t be sure from it just appearing on the page. You need to test it now too.
We are still in the domain of simple websites. And this is getting too long. Let me just through a few more things at you:
- more content (imagine a website with dozens or hundreds of pages … this very blog has almost 10,000 blog posts, which are organized into categories, tags, date archives, etc).
- more functionality (fancy things, dynamic page loads, form validations, etc)
- even more functionality (online shop, user-driven content, etc)
- more integrations with other services (Google, social networks, company CRM/ERP/etc)
- spreading the site across multiple servers for performance (multiple web servers, caching servers, application servers, database servers, etc)
With each and every bit that you throw into your website, the testing gets exponentially more complex. You have to consider functionality testing, user interface testing, performance testing, security testing, and so on and so forth.
When you get to all of that, you probably have multiple people working in several teams. They all need to communicate and coordinate. Which is another layer of complexity.
I’ll stop here.
Next time you think testing is easy, think again.
Update (September 10, 2016): here are a few more misconceptions, which are as common as the ones above.